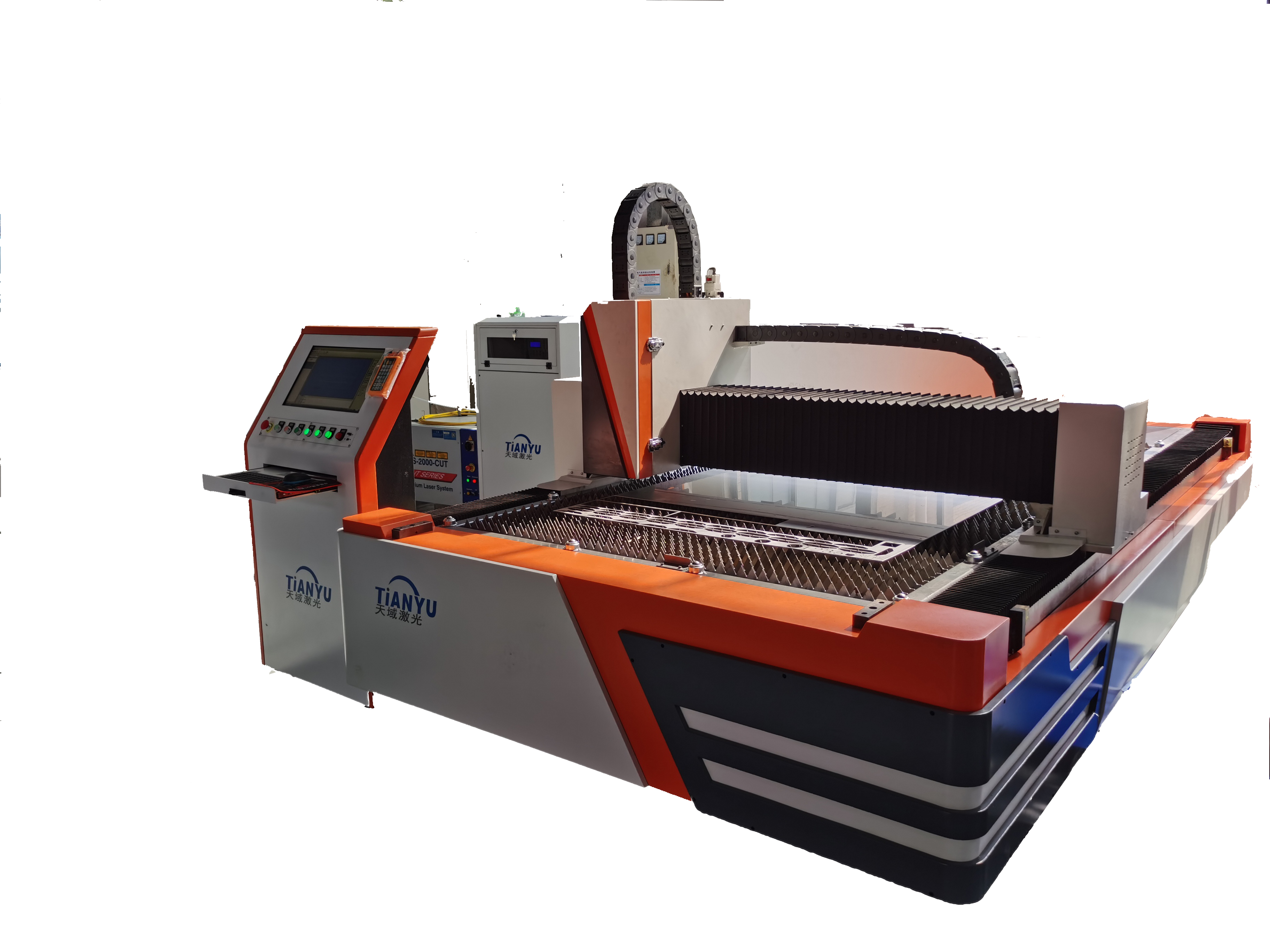
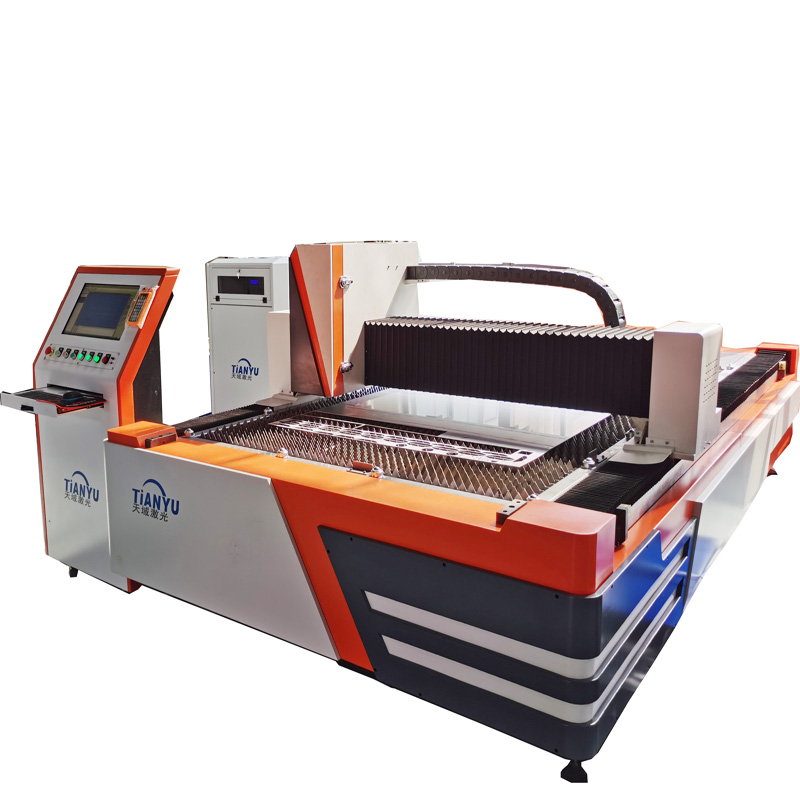
One Laser, Multiple Applications
A single laser can perform multiple laser processes. To achieve this, our experts make small adjustments to the laser parameters and to the optical components.
This simplifies and speeds up integrations, as the same laser system can be used for all your integrations. In addition, all lasers use the same controller module. This allows system integrators to work in the same environment when connecting cables and programming data exchange.
- One Laser, Multiple Applications
- Laser cleaning
- Laser welding
- Laser marking
- Laser cutting
AboutLaser cutting machineType Frequently Asked Questions
Buy fiber optics or CO₂?
1) Material Determination: For metals > 1 mm, fiber is preferred (metal absorption at 1 µm wavelength is > 80%); for non-metals (acrylic, cloth, glass), CO₂ (10.6 µm) is preferred. 2) Thickness: Fiber > CO₂. For carbon steel > 6 mm, the speed advantage is significant (measured speed at 6 kW for fiber cutting 12 mm of carbon steel is 1.8 m/min, while CO₂ is only 0.4 m/min). 3) Operating Cost: Fiber's electro-optical conversion efficiency is 30-35%, while CO₂'s is only 10-12%. Each kilowatt-hour of electricity cuts approximately 2.7 times the length of fiber compared to CO₂.
How much power should I choose?
1 kW can stably cut carbon steel 6 mm and stainless steel 3 mm; 3 kW can cut carbon steel 20 mm and stainless steel 10 mm; 6 kW can cut carbon steel 25 mm and stainless steel 20 mm.
Cutting accuracy suddenly drops
Priority checks: ① Rack wear (use a feeler gauge to measure backlash, >0.1 mm requires adjustment); ② Servo motor encoder feedback (use a laser interferometer to measure positioning accuracy); ③ Machine tool temperature (thermal elongation 0.02 mm/m at >35°C).
What should I do if the laser has no output, overheats, makes noise, alarms, or has power reduction?
If there is no output, check the power supply/connection/cooling system; if it is overheated, check the filter/coolant; if it is noisy, check the fan; if it is an alarm, check the signal line; if it is a power drop, check the lens for dirt or power fluctuations. Regular maintenance