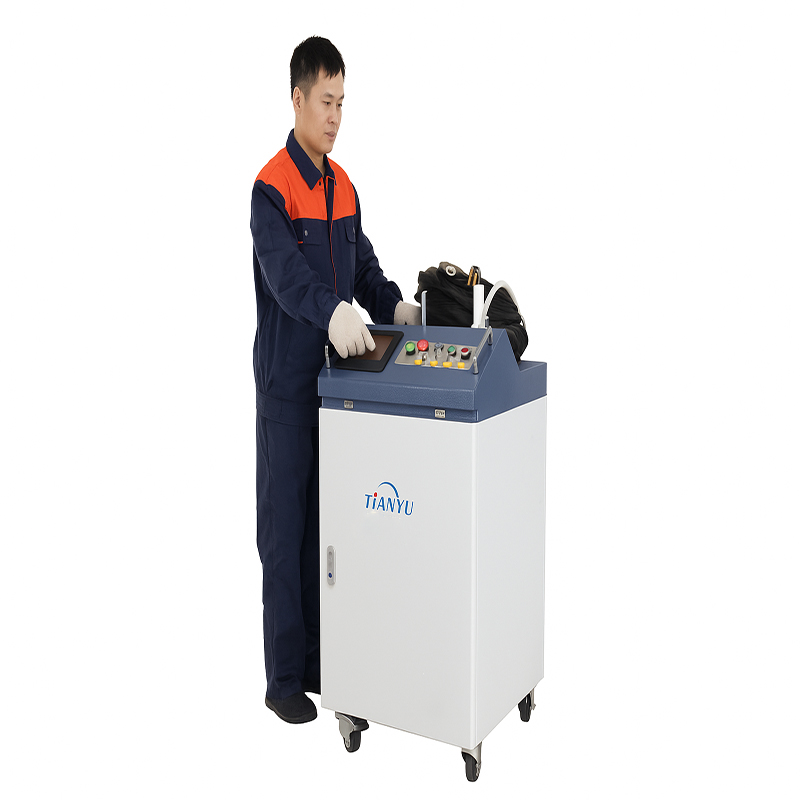
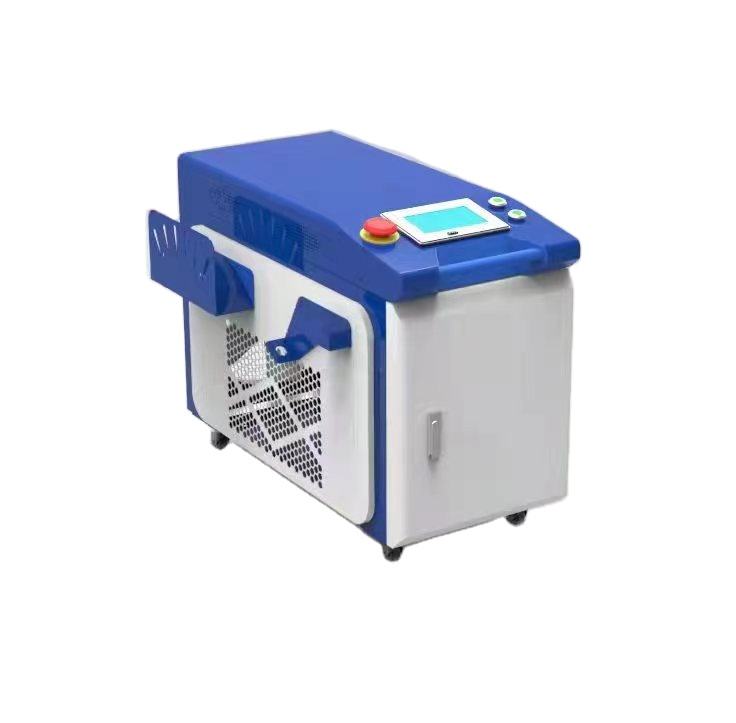
Continuous cleaning machine
The specific process involves several reactions:
Evaporation: The laser beam heats the contaminant to its vaporization temperature, converting it directly from a solid or liquid state to a gaseous state.
Ablation: The laser energy weakens the bond between the contaminant and the substrate, causing the contaminant to be removed from the surface.
Decomposition: The laser energy triggers the chemical decomposition of the contaminant, converting it into harmless substances.
Since the substrate typically absorbs little or no laser energy, its surface remains intact. This cleaning method is highly efficient, environmentally friendly, and does not damage the substrate.